PSD3 updates: Deep dive on fraud prevention, bank liability, and the regulatory impact

The Authentication Newsletter for January 2026
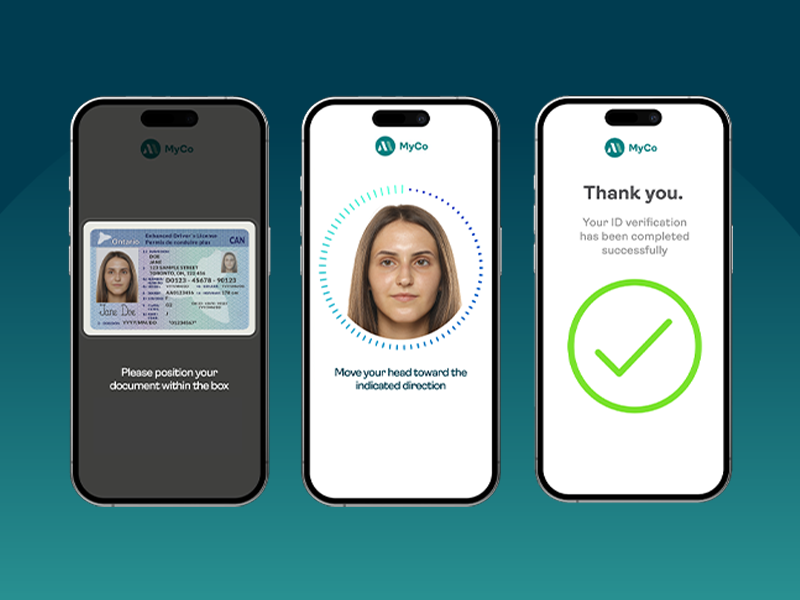
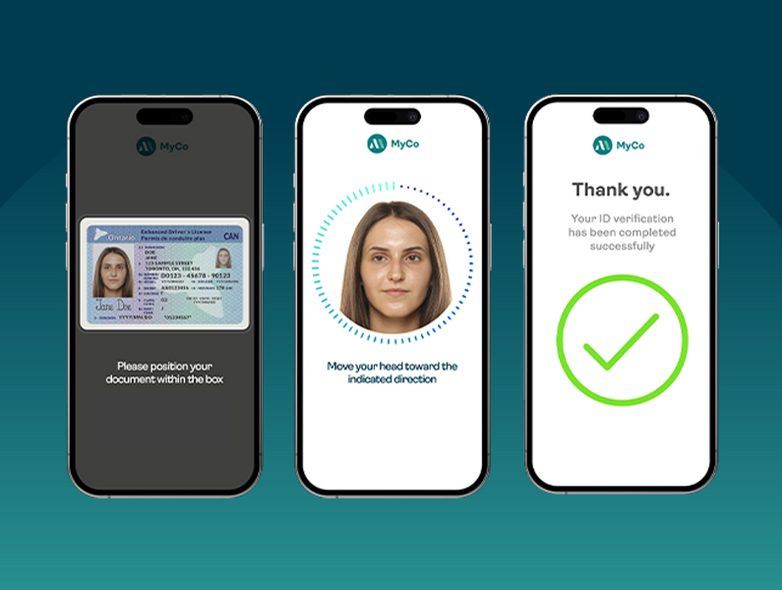
FINTRAC: Preparing your identity verification strategy for more than just compliance

Passkeys implementation: Build or buy?

Pros and cons of passkeys: Security benefits outweigh risks

Beyond authentication: Why device and behavioral intelligence are now non-negotiable for banks

FINTRAC’s identity verification guidance is a timely step forward—but compliance will require legwork