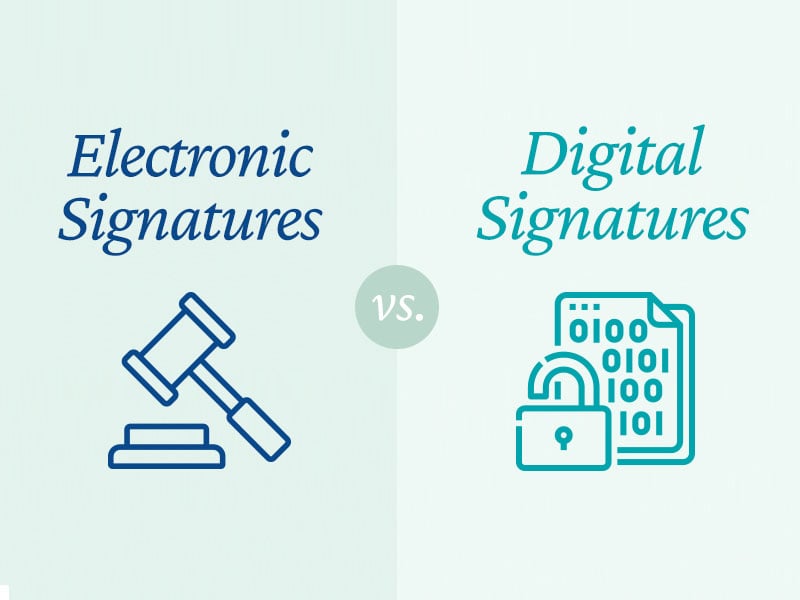
The difference between eSignatures and digital signatures

As our world grows increasingly dependent on digital systems, business has become more automated. The past decade witnessed a surge in businesses transitioning from paper-based processes to digital. eSignatures are at the forefront of this change.
However, there are still misconceptions about the difference between eSignatures and digital signature technology. Most people see these terms as synonyms but they are distinct, and this is evident in their core functions.
What is an electronic signature?
An electronic signature is, like its paper equivalent, a legal concept. In the U.S., an eSignature is an electronic sound or symbol or process used to sign a document. U.S. law recognizes an eSignature as a valid form of signature. It allows individuals to sign documents electronically instead of using a handwritten signature.
What is a digital signature?
The term digital signature, on the other hand, refers to the encryption technology that an electronic signature solution uses.
A digital signature alone is not a type of electronic signature. Rather, a digital signature secures the data associated with a signed document. It helps ensure that a signed record is authentic.
When used alone, a digital signature cannot indicate a person's intent to sign a document. It also cannot show the legal obligation to an agreement or contract.
Software that simply digitally signs documents lacks features found in eSignature solutions, such as advanced workflow capabilities. When choosing electronic signature software, make sure it uses digital signature technology. This preserves the integrity of the document and signatures. Without digital signature technology, your eSigned documents may not be legally binding.
What is a digital certificate?
Digital signatures use a system called public key infrastructure (PKI). This system involves public and private keys that keep digital transactions safe and secure.
When you sign a document online, you want to know that both the signed document and the signers are authentic. That’s where the role of the digital certificate comes into play.
The purpose of a digital certificate is to validate and certify that an eSignature corresponds to a specific signer. It contains data related to the identity of signer (e.g., name, ID number, signature keys, certificate issuer, etc.).
You need the digital certificate to create a digital signature.
For processes that need the highest levels of security, personal digital certificates are a way to authenticate the signer. To get a personal digital certificate, the signatory applies to get one from third party certificate authorities (CA). In the European Union, the issuer is a Trust Service Provider (TSP).
Types of digital certificates
Depending on factors such as geography, industry, and risk, organizations will use different types of digital certificates.
There are two types of digital certificates used for signing documents:
- Server-signing certificate: The signer is authenticated and the document is digitally signed using the eSignature vendor's trusted certificate. It is stored in the cloud.
- Local-signing certificate: The signer’s identity is attached to a personal certificate. Their personal certificate is stored locally on a PIN-protected smart card, USB token, or computer. That person uses the certificate when eSigning the document.
According to Forrester, "The US predominantly opts for simpler eSignature authentication". The US has opted for the advanced eSignature (AES). AES can use different authentication methods along with a shared server-signing certificate stored in the vendor's cloud service.
The European Union, on the other hand, "places a higher priority on authentication".
The EU may require an AES coupled with strong forms of authentication.
Higher-risk processes require the qualified electronic signature (QES), which relies on third-party digital certificates. In Belgium, authorities issue citizens electronic identity (eID) cards that include a unique digital certificate. People use these for different purposes, including signing contracts.
The importance of digital signatures
The eSignature software should apply the digital signature at two levels:
- At the signature level to prevent tampering with the signature itself
- At the document level, to prevent tampering with the document’s contents
This double layer of security ensures the integrity of the document. With tamper-evident controls such as these, you can trust the integrity of a signed document.
eSignatures are only as good as the security that protects them. That is why any changes to the document, like adding or removing words or pages, will visibly invalidate it.
Protect the digital agreement at two key points
Digital signature technology is one of the most important components of an electronic signature tool.
Digital signatures underpin security and legal validity. The creation of an electronic signature should not happen without the backing of a digital signature.
Here are three reasons why digital signatures hold such significance:
1. Safeguarding the signature during the signing process
A digital signature is a secured file that accompanies the electronic document and is part of it.
The file holds and records metadata about:
- The journey of the electronic document
- Who accessed it
- The IP address of the devices that signed it
- The exact timing of the interaction
- And other vital information
All of this data ensures the authenticity of the signature.
A digital signature also captures information such as the device that a document is signed on and the signer's credentials. This information provides multiple tiers of signature verification, protecting the signing process in entirety.
2. Safeguarding the signature in storage
Businesses and governments need to store signed records for a certain amount of time. The duration varies based on specific industry laws.
You must be able to verify that nothing in the signed document has changed over time. A digital signature that is attached to the electronic signature will show whether the content has been tampered with.
Not all electronic signature options are the same, and some don't have long-term validation capabilities. Make sure that the solution you choose meets the following digital signing requirements:
- A digital signature should be embedded into the eSigned PDF for each signer in the transaction.
- Each entry should include details such as the signer's digital certificate, a timestamp, and the signer's information.
- Signed documents should be able to be verified offline, independent of the e-signature solution. Look for "Signature is LTV enabled" in the signature panel of the e-signed PDF.
Meeting regulatory requirements
Organizations in sectors like government, healthcare, and financial services always have regulatory concerns to keep in mind. They must adapt their operations in light of legal guidelines impacting the industry.
Government agencies, hospitals, and banks are digitizing at a breakneck pace. Most no longer print documents, mail them, get them signed, and store them in vaults or warehouses.
As organizations transition away from legacy document processes, they must meet regulatory guidelines. But regulatory plans get tricky because most regulations don't tell you how to comply, they tell you the result you need to get.
Regulated organizations need to find technologies that get them the results they need.
Protecting data in transit often involves the use of encryption. Effective authorizations are also key. Digital signatures provide these functions. Because digital signature technology is part of eSignature software, it makes eSignatures a perfect fit in many regulatory settings.
Putting it all together
eSignatures and digital signatures work together to keep signed documents safe, secure, and easy to verify. As a result, people can easily sign documents without worrying about whether their contracts will be valid and enforceable.
There are many eSignature options that meet the basic requirements of the ESIGN Act (Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act). However, organizations should strive for one that includes digital signature technology.
We also have a handy infographic detailing the differences and how they work together.