Resource Center
This company set out to address several challenges when evolving its customer authentication strategy to serve a growing customer base across a diverse set of product offerings and user personas.
Smart Sense introduces intelligent risk detection to modern authentication
Passwords aren't just inconvenient anymore, they're dangerous. The good news: The solution is here.
Learn how mobile threat intelligence and real-time prevention strategies stop account takeover, impersonation scams, and voice phishing attacks at every stage of the attack chain.
With the OneSpan Multi-channel Notification feature, send SMS and email notifications to reach signers in their preferred channels.
One conversation, three perspectives on securing mobile apps. Watch this webinar for a behind-the-scenes exchange on how strategic decisions are shaped.
This white paper explores a third option: a hybrid strategy that lets you deliver a differentiated UX while relying on a proven, secure foundation for passwordless authentication.
In this white paper, learn how passkeys deliver phishing-resistant protection by design, eliminating passwords and neutralizing threats like credential theft.
Silverfort and OneSpan demonstrate how adaptive access control combined with hardware-backed, phishing-resistant MFA can significantly reduce ransomware risk even in hybrid and legacy-heavy
Simpler logins, stronger security—powered by passkeys and beyond.
Watch this webinar to discover how forward-thinking organizations are revolutionizing their agreement workflows through SMS Notifications.
Simplify the claims experience with mobile-friendly eSignature, smart forms, and guided workflows.
Watch this webinar to discover how modern agreement technologies are transforming the onboarding and account opening process.
Stop account takeovers, reduce social engineering, and safeguard customer trust with cutting-edge authentication.
Banking-grade cybersecurity solution for phishing-resistant authentication and advanced transaction verification on a trusted display.
The question is no longer if you’ll adopt FIDO (Fast Identity Online), but when. Learn how leading banks and insurers are moving now — and how OneSpan can help you get there.
Learn how FIDO-based passkeys deliver phishing resistance, facilitate regulatory compliance, and generate measurable ROI.
Watch this webinar to discover OneSpan’s latest innovations to deliver smarter, seamless, and fully-digital eSignature experiences.
Phishing-resistant authentication that complies and exceeds NIS2 requirements
Research report reveals 67% of enterprises have started passwordless authentication journeys. Download insights on workforce security trends and ROI benefits.
How Onespan’s Digipass® hardware authenticators help banks comply with the European Accessibility Act
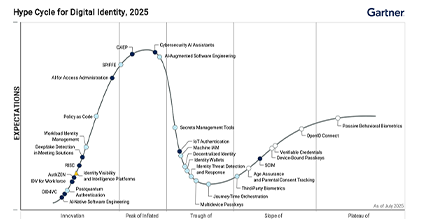
The latest Gartner Hype Cycle explores where digital identity is headed – from AI-native platforms to decentralized credentials – and what security leaders need to pay attention to next.
Learn about the CBUAE’s new regulatory requirements.
Phishing-resistant and passwordless authentication with Amazon Web Services
Phishing-resistant and passwordless authentication with Google Workspace
In this video, we show you how to log in to Ping One your Digipass FX7.
In this video, we show you how to register your Digipass FX7 for secure access to Ping One.
In this video, we show you how to set up your Digipass FX7 for Ping Identity FIDO Policies.
In this video, we show you how to log in to Okta with your Digipass FX7.
OneSpan Sign is the preferred eSignature solution for OEM vendors.
In this session, we explore how FIDO authentication addresses today’s critical security gaps in workforce access and transaction approvals.
A first-ever global call for stronger workforce authentication
In this video, we show you how to set up your Digipass FX7 for Delinea Identity Policies.
In this video, we show you how to logon to OneLogin with your Digipass FX7.
FIDO2 passwordless authentication. What's the difference between syncable and device-bound passkeys?
This top 10 North American bank provides banking, wealth management, insurance, and other services to millions of customers globally.
Integrated Signing Platforms: Taking eSignature to the Next Level with iPaas Driving Higher ROI and Adoption with an Enterprisewide Digital Agreements Platform Amy Machado Senior Research Manager
Learn how iPaaS solutions unlock new levels of efficiency and flexibility in eSignature workflows.
6 technology best practices from 5 insurance and financial services providers. Learn how tech transformed their paper-heavy ecosystems, starting with first-day processes designed for digital channels.
Learn how to modernize your HR processes with OneSpan Sign integrated with Workday.
OneLogin and Digipass® FX: Secure, passwordless authentication
Our five-step guide will help you smoothly and effectively navigate the transition from planning through migration.
See OneSpan's pre-built eSignature integration for Workday in action.
In this session, we’ll explore the latest mobile threats, real-world attack scenarios, and best practices for protecting your devices and data.
Stop account takeovers, eliminate passwords, and secure your workforce with DIGIPASS® FX.
Our experts showcase the latest advancements in OneSpan's digital agreements offerings.
Guidewire and OneSpan discuss leading your organization through a successful cloud transformation.
Watch our demo webinar, where we showcase how eSignature, Smart Forms, and Identity Verification are transforming the onboarding and account opening process.
Signers can now use a FIDO passkey to confirm their identity before eSigning documents.
OneSpan explores how passwordless solutions built on FIDO standards can address key challenges and elevate security, improve user experience and add compliance to regulations such as NIS2.
How NIS2 & DORA Impacts Your Customers – Best Practices ~ FX Passwordless Authentication
Opening a new account is easy, fast, and secure with eSignatures, digital ID verification, and smart forms.
Digipass FX is a phishing-resistant, passwordless authentication device based on the FIDO2 standard.
This paper provides digital banking, security, and fraud experts with an overview of the most important anti-scam regulations around the world.
New types of banking and payment fraud have prompted EU regulators to review and adapt PSD2. Get an update on the state of this regulatory overhaul.
BMO has long been a leader in digital innovation and won awards for its approach to eSignature and eForms deployment
Get a headstart evaluating eSignature security features with this checklist that covers 6 security categories and more than 20 requirements.
Send documents for eSignature from accounts, policies, and jobs – no need to leave familiar workflows in PolicyCenter.
Phishing-resistant and passwordless authentication with Microsoft Entra ID
Transform outdated claims processes into easy interactions that customers love - all without leaving ClaimCenter.
See how OneSpan's pre-built integration for SharePoint boosts employee productivity and strengthens recordkeeping, compliance, and auditability.
In this video, we show you how to set up your Digipass FX7 for secure access to the OneLogin platform.
In this video, we show you how to set up your Digipass FX7 device for Entrust.
Discover how these integrations streamline HR operations, enhance productivity, and simplify compliance.
In this webcast, our experts explain how to achieve higher customer completion rates using OneSpan Smart Forms.
OneSpan Sign for Greenhouse is an out-of-the-box eSignature integration with Greenhouse Recruiting.
An out-of-the-box eSignature integration with Google Workspace applications, such as Google Drive and Google Sheets.
An out-of-the-box eSignature integration with Microsoft applications such as SharePoint Online, Dynamics 365, and OneDrive.
OneSpan Smart Forms transforms paper-based forms into efficient digital versions, improving the customer’s experience with pre-fill abilities using saved information from core systems, digital
Use a single solution to connect eSignature to your favorite business applications in an easy, secure, and cost-efficient way.
Stop account takeovers, protect your employees and applications, and eliminate passwords with Digipass® FX7, a FIDO-enabled, phishing-resistant authenticator.
In this video, we'll show you how to securely log on to Windows using Digipass FX7.
In this video, we'll show you how to securely log on to Microsoft Office 365 using Digipass FX7.
In this video, we'll explain how to set up your Digipass FX7.
In this video, we'll explain how to set up your Digipass FX7.
Learn how to log on to AWS on your Android phone using Digipass FX7.
Introducing Digipass FX1. Go passwordless with FIDO-based, phishing-resistant authentication.
See how to set up your Digipass FX1 security key, step by step.
As a global corporation with operations, customers, and suppliers worldwide, OneSpan understands that active management of our environmental and social impacts and risks is fundamental to our long
OneSpan's second annual environment, social, and governance (ESG) report includes information about how we evaluate our environmental impacts, manage cybersecurity risk, and more.
See how to use this integration to get a corporate policy document signed and automatically stored back in Workday.
See how to use OneSpan Sign for Greenhouse to send an offer letter for signature directly from Greenhouse.
Get started with OneSpan's out-of-box integrations for Google Drive in minutes. See how it works in this demo video.
Hear OneSpan's Field CTO Will LaSala speak with Expert Insights about why businesses should switch to FIDO as a stronger, more intuitive authentication method.
Our expert panel dives into innovative solutions, discussions and demos of out-of-the-box Microsoft SharePoint and Google Drive integrations.
Join our product experts as they host the OneSpan 2024 H1 Innovations webinar, unveiling our latest innovations across our Digital Agreements portfolio.
To maintain security, while enhancing the customer journey - digital agreements are evolving to deliver omnichannel experiences, backed by digital identity and legal enforceability.
In this mortgage application demo, see how much faster, easier, and more secure it is for the customer to complete and sign forms-based agreements.
Learn how to use this FIDO2 security key to log in to Microsoft Entra ID.
In 1 minute, learn how to use this FIDO2 security key to log on to Amazon Web Services.
Learn how to use our latest passwordless authenticator to log in to Office 365.
Learn how to use our latest passwordless authenticator to log in to Office 365.
Learn how to use our latest passwordless authenticator to log in to Cloudflare.
Learn how to use our latest passwordless authenticator to log in to your Windows account.
Our digital transformation experts guide you through the fundamentals of IPEN and its innovative approach to notarizing documents.
We review top capabilities, essential requirements and other considerations to create an unmatched online notarization experience.
Essential aspects of PSD3 and anti-fraud measures, offering you the knowledge and skills to stay ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of digital finance.
Digital transformation experts covered the benefits of modernizing the traditional notarization process to deliver a convenient, secure and compliant online notarization experience.
OneSpan’s Field CTO delivers a keynote about improving the ease and security of digital customer conversations.
In this report, we share best practices from organizations that have transformed account opening – so you can improve your customer experience, facilitate compliance, and reduce the risk of fraud.
OneSpan and Smart Communications share how the complex data collection and agreement processes of today can be quickly and easily digitalized for the customers of tomorrow.
OneSpan & ISMG take a deep dive into the key drivers for businesses investing in strong workforce authentication solutions.
Discover the power of streamlined eSignature integrations with OneSpan, providing a cost-effective solution for boosting productivity.
Frederik Mennes, Director of Product Management and Business Strategy at OneSpan, shared insights on upcoming banking regulations in Europe and their implication for financial services companies.
Learn about NIS2 and DORA regulations and MFA solutions for workforce security.
An end-to-end solution that strengthens organizational security, unifies authentication experiences across channels, and effortlessly adapts to evolving security demands over time.
In this video tutorial we’ll show you how notaries can conveniently notarize documents electronically with signers in a face-to-face scenario.
Learn how NIS2 and DORA regulations impact your business, and why compliance is crucial to avoid heavy fines.
Stop account takeover attacks and protect employees, partners, and corporate resources with Digipass FX1 BIO.
In this webinar OneSpan explores how digital agreements can play a key role in driving businesses cost optimisation programme, both saving money and increasing efficiency.
The European Commission recently released the much-anticipated draft proposal for PSD3, the next iteration of the Payment Services Directive (PSD2). Watch the recording of our webinar to get an update
To help guide your search for an esignature solution, IDC has analyzed over 20 esignature vendors and named OneSpan a leader in the IDC MarketScape Worldwide eSignature Software 2023 Vendor Assessment
OneSpan reviews top capabilities, essential requirements and other considerations to create an unmatched online notarization experience.
Enterprise users rank OneSpan Sign higher vs. DocuSign in the capabilities that matter most. When it comes to ease of use, quality of support, and custom branding (white labeling), we lead the way.
Account opening and customer onboarding typically is the first touchpoint with a bank or business for most customers and it is critical to get this right. However, many organizations are limited by
In the second of this 2-part webinar series, we uncovered ways for moving beyond your initial e-signature use case and identify the right set of next use cases to tackle.
In this first of 2 webinars, digital business experts from OneSpan share tips to ensure e-signature adoption for existing and future workflows.
Digipass GO 7 FIPS is a FIPS 140-2 Level 2 Certified one-time password (OTP) hardware token – a convenient single-button authentication device that boosts security while providing unmatched user
Digipass 795 offers an ideal solution for banking customers who create and verify numerous transactions multiple times a day.
See how OneSpan Sign and ID verification can be used to digitize point of sale and picking for the warehouse and distribution industry.
Presented on: Tuesday, June 6, 2023. Today’s customers are pushing businesses into the Web3 world and increasingly looking to complete agreements – even notarizations - digitally. With over 1 billion
Presented on: Monday, June 12, 2023. Presenters: - Will LaSala, Field CTO, Americas OneSpan - Nick Barradale, Regional Sales Manager, OneSpan Today’s customers are pushing businesses into the Web3
OneSpan is a leader. Get your copy of the 2023 Aragon Research Globe™ for DTM to learn why OneSpan Sign outperforms with secure, easy e-signatures for the enterprise.
Today’s enterprises are facing tremendous pressure to modernize so that they can unlock their capacity for better, more profitable customer experiences. The fact is, they’re being challenged to adapt
In this webinar, an impressive trio of mobile app experts share strategies to help organizations follow a mobile first mindset, which includes app shielding that keeps apps protected from unknown
In this interactive fireside chat, OneSpan Field CTO Will LaSala shares perspectives for financial services professionals on why cybersecurity needs to be thought of holistically in order to be
Meet rising demand for the shift to digital notarization with OneSpan Notary. Watch the video to learn more.
Transform your notarization process for greater efficiency and superior experience. Get this essential guide to remote online notarization for industry best practices, FAQs, and tips to get you
As a notary, see how to validate a signer’s identity using ID verification and KBA for remote online notarization (RON).
In this webinar, digital transformation experts from OneSpan cover the benefits of modernizing the traditional notarization process to deliver a convenient, secure and compliant online notarization
What you'll find in this guide: The benefits of secure and compliant eSignatures Learn how modern paperless processes can lead to higher adoption by employees, users, and constituents. Top 5 questions
In this webinar, discover the benefits of modernizing the traditional notarization process with OneSpan Notary to deliver a convenient, secure and compliant online notarization experience to signers.
Our Enterprise Elite Package provides the highest level of customization with a dedicated team focused on your organization’s success and growth.
Our Enterprise Essential Package provides around-the-clock support for critical incidents, and access to our seasoned technical consultants.
Our Core Package provides access to the highly experienced OneSpan customer success team, along with self-service support resources that are designed to set you up for success and growth.
OneSpan’s success packages are offered in a tiered approach providing the full range of benefits and resources you will need during your partnership with OneSpan.
This webcast explores the top processes for credit unions to successfully digitize, including how to replicate in-person transactions with a hybrid model that combines digital with a human touch.
In this webinar, a duo of digital integration experts share best practices for filling the technology gap and augmenting platform capabilities by leveraging best-in-class, partner-friendly
In this video tutorial we’ll show you how to access electronic evidence in OneSpan Notary after the remote online notary session has been completed.
In this video tutorial we’ll show you how easy it is for a notary to complete a Remote Online Notarization session with a signer.
In this webinar, a team of mobile experts from OneSpan and Promon share how and why organisations should integrate mobile app security technology that continually monitors apps as they operate
In this video tutorial we’ll show you how easy it is for a notary to configure a transaction for Remote Online Notarization (RON).
See how administrators can onboard a notary to start using OneSpan Notary.
In this webinar, a team of digital solutions experts share strategies on how to optimize digital HR processes while ensuring the human element remains at the centre of remote exchanges.
In this webinar, discover ways to overcome the challenge of replicating in-person experiences via remote channels, and modernize client interactions during the procurement process wherever they take
In this webinar, industry experts share how eSignatures can help healthcare organizations streamline their processes, while improving efficiencies and maintaining the highest levels of security and
In this webinar, a team of mobile experts from OneSpan and Promon share how and why FIs should integrate mobile app security technology that continually monitors apps as they operate, bolstering their
In this demo, a notary will remotely notarize an affidavit with a signer using OneSpan Notary.
In this interview with Harold Sinnott, we discuss how OneSpan Notary was designed with input from notaries -- and how that helped optimize the user experience while building protections against
Transform how your notaries and customers get agreements completed – easily and securely, in a trusted environment
OneSpan Field CTO Dan McLoughlin discusses the mobile application threat landscape – and what developers can do to secure their apps.
Over 60% of the world’s most popular finance apps are vulnerable to repackaging attacks, according to Promon Research. Learn what benchmarks you should use to assess your level of app protection.
Learn how one division of a global enterprise is integrating e-signatures with SAP Human Capital Management (HCM) for end-to-end digitization of recruiting and onboarding.
In this webinar, learn best practices for filling the technology gap in your platforms by seamlessly embedding e-signature, ID verification and user and transaction authentication technology.
In this webinar, experts share insights on embedded lending and customer experience.
In this webinar, digital business experts will explore the ways to rapidly extend those benefits to additional business lines, channels and use cases.
In this webinar, our panel of industry experts provide insights in the opportunities presented by the trend toward higher-value online transactions, the risks, compliance, and customer experience
In this webinar, digital business experts will explore why teams need to get behind this digital revolution and share tips to ensure adoption for existing and future workflows.
In this webinar, learn how to overcome the challenges surrounding digital agreements and the need for higher assurance to boost security and customer satisfaction.
OneSpan has been recognized with the 2022 North American Product Leadership Award in the continuous passwordless authentication industry. Get your copy of analyst firm Frost & Sullivan's report to
Remote loan closing has become one of the most sought-after capabilities in mortgage lending. Indeed, many consumers are seeking alternatives to the traditional loan closing ceremony, with about half
The banking, financial services and insurance (BFSI) industry was forcibly plunged into remote working arrangements for the past few years due to the pandemic. Remote work will most likely still be
In this webinar, a duo of digital agreement experts explore the top processes that manufacturers are digitizing, and how they are delivering seamless digital journeys for their customers and employees
In this webinar, you'll learn how to overcome the challenges surrounding digital agreements and the need for higher assurance to boost security and customer satisfaction.
In this webinar, digital experts share the top processes for credit unions to digitize, including how to replicate in-person transactions with a hybrid model that combines digital with a human touch.
Rethink how you process information and capture consent in your digital customer journeys with OneSpan and Smart Communications.
Find out how business leaders are adapting to the threats of today's digital landscape, with cybersecurity expert Shira Rubinoff
In this webinar, you’ll discover ways for banks and FIs to overcome the challenges that come with replicating in-person experiences via remote channels, and modernize how you can interact with clients
Hear how Buy Way cut point-of-sale contracting time from 20 days to 10 minutes with electronic signature.
In this webinar, digital experts from OneSpan and Smart Communications discuss how client expectations are evolving in wealth management and how advisory firms are automating digital agreements in
Learn how to optimise the digital customer experience, addressing the different aspects of friction and merging the two worlds of digital and physical.
In this webinar, digital business experts share best practices for organizations looking for ways to rapidly extend e-signature benefits to additional business lines, channels and use cases.
Digipass 750 Comfort Voice is a voice-enabled connected hardware device especially designed for visually impaired and blind people. This solution enables banks to provide the same authentication and
In this hour-long webinar, Richard DeMello, the e-signature administrator for the Michigan Department of Technology, Management and Budget, outline step-by-step how to roll out an electronic document
In this webinar, a duo of digital agreement experts share how the auto retailing and finance industry is investing in innovation that dramatically improves the customer experience, increases
A panel of experts discuss the dynamics driving Super Apps in the marketplace and where they think the technology is headed in this webinar.
In this webinar, digital business experts explore why teams need to get behind this digital revolution and share tips to ensure adoption for existing and future workflows.
Find out how e-signatures, virtual rooms and digital identity verification can enable the digitization of complex agreement processes that require remote online notorization.
Watch this webinar to explore and hear from practitioners on how they are reinventing their insurance business.
Industry experts from OneSpan and Smart Communications share top digital transformation trends that deliver truly superior customer experiences in insurance.
In this webinar, a team of digital business experts from OneSpan provide a comprehensive review of e-signature workflows, as well as customization and authentication options.
Learn how financial institutions are turning to applications, open APIs, and fintech solutions to deliver specialized and engaging customer experiences, reduce costs, and meet consumer’s rising
In this webinar, our security experts will discuss mobile malware types and which processes, technologies and strategies can be used to protect your customers.
Outdated yet ubiquitous, passwords are inconvenient, risky, and costly for banks to maintain. So what’s the best way for banks to modernize authentication with secure and user-friendly password-less
Easily integrate SmartIQ and OneSpan Sign to create an intelligent, interview-style digital form with e-signatures, making it easy for customers to review and sign documents.
See how Santander’s dealers get auto finance agreements signed digitally using electronic signature from OneSpan.
Get the latest information during this hour-long webinar presented by Government Technology and OneSpan where experts in digitization take a deep dive into utilizing digital transformation projects to
In this webcast, experts explore how to modernize digital processes and review the top digitization trends and technologies that are reshaping the insurance ecosystem.
Financial institutions have a challenge to defend against this level of mobile banking malware but it is possible with updated authentication and security frameworks, live analysis and monitoring
See this short video to learn how OneSpan Sign for Laserfiche accelerates and secures digital agreement processes between customers, internal signers, or external suppliers.
OneSpan Sign for Laserfiche Cloud allows you to prepare, manage, and send documents for e-signature directly from Laserfiche. Using OneSpan Sign for Laserfiche, you can now better collaborate with
In just 2 weeks, this bank setup an online enrollment process for suppliers, using e-signature and digital forms. Learn how with OneSpan Sign for SmartIQ.
In this webinar, industry experts review top digitization trends and technologies for 2022 that are reshaping the digital insurance ecosystem.
In this webinar, expert speakers share how to overcome the challenges of replicating the in-person experience via remote channels, and modernize how you interact with your clients.
Asian Financial Institutions are increasingly offering more complex services via the mobile channel in their quest to attract and retain new banking customers faster. On the other hand, disruptive
As carriers and broker-dealers focus on their digital transformation priorities, completing agreements is at the center of insurance. Whether completing a standard auto insurance policy or a complex
In this fast-changing world, with soaring pressures to be customer-centric, how does government keep up? This session examines evolving expectations and how they will affect the future of government
The pandemic has accelerated digitisation across industries, with financial services seeing an outsized impact. With traditional in-person channels unavailable and the need to support a global remote
Consumer finance lenders face unique challenges: evolving consumer behaviours, intense competition, and obstacles to digitize loan and credit processes. These challenges have accelerated the need for
Financial services are converging on the mobile channel. As such, the mobile app has become the key channel for many banking providers and the pandemic has only ramped up the pace and pressure in this
In this webinar, a team of digital government experts share tips for how state and local government can streamline their processes, cut costs, and increase security with e-signatures.
SC Ventures implemented SC eSign across 21 countries and 40 processes within the bank.
In this webinar, a team of digital business experts from OneSpan provide a comprehensive review of e-signature workflows, as well as customization and authentication options.
ID verification can be used to validate a signer’s identity before they access documents. Get an overview of this feature.
30 days after replacing DocuSign as their e-signature provider, this insurer saw a 23% increase in completion rates. The reason: white-labeling.
Get life insurance applications closed in under 24 hours. See how Generali uses electronic signature to accelerate the application process.
OneSpan Sign includes ID verification as a signer authentication method. See how it works, step by step.
Accelerate business processes by adding eSignatures to your HR workflows
This digital bank relies on strong customer authentication and mobile app security from OneSpan. Learn more on OneSpan's Cronto technology and PSD2 expertise.
Watch this video to learn how OneSpan’s cloud-based multi-factor authentication solution helps financial institutions reduce fraud and improve the user experience.
The Great Lakes State deployed OneSpan Sign as a shared service to facilitate the launch of new e-signature workflows
In this podcast, hear from OneSpan and Oliwia Berdak, VP and Research Director at Forrester, on how to adapt your digital transformation to customers’ changing needs.
This leading auto financier cut processing time 70% by equipping dealerships with electronic signature. The result: fewer errors and greater convenience.
The State of Michigan relies on electronic signature for contracts and procurement. Hear from the e-sign admin at the Michigan Department of Technology.
Do you require your signers to provide additional supporting information to a transaction like a copy of their driver’s license or medical card? OneSpan Sign offers the ability for signers to upload
Learn how OneSpan Sign for Laserfiche accelerates and secures digital contracting processes
This e-signature Readiness Guide will help you carefully evaluate each e-signature implementation option, including any associated technical requirements.
OneSpan Sign’s integration with eOriginal’s electronic vaulting service allows users to manage high-value digital assets like loans, leases, and mortgages. After a document is e-signed using OneSpan
OneSpan Sign offers an additional signature option giving signers the ability to upload an image of their signature when completing transactions. Signers can scan an image of their signature and
Learn how Cronto visual transaction signing from OneSpan be used to help prevent social engineering attacks.
This case study explores how Odeabank improved user experience and security while reducing SIM swap and other fraud attacks.
OneSpan Sign is the fast and secure way to get documents signed anytime, anywhere.
This video demonstrates the combined value of OneSpan’s Intelligent Adaptive Authentication and Risk Analytics technologies and ForgeRock’s Access Management Platform.
Loan Market achieved paperless mortgage lending in Australia with OneSpan Sign electronic signature. Learn about their digitization journey.
When a transaction is sent to a predefined group of users, any group member can eSign on behalf of the group.
Around 40% of MotoNovo's new business is now fully automated, leading to significant growth.
Signers can review documents on a PC, then provide a handwritten signature on their mobile device.
In this step-by-step tutorial, see how easy it is to create and save a handwritten signature in OneSpan Sign.
The centralized administrator panel gives you control over your entire OneSpan Sign account, across your organization.
Transcript: Out of Bank Authentication with Push Notification With data breaches still on the rise, organizations need to take appropriate measures to secure internal and remote network access for
Sony Bank takes the security of its mobile banking app seriously. To protect against attacks, they use OneSpan's mobile app shielding with runtime protection.
The Business Development Bank of Canada integrated electronic signature into their mobile app so entrepreneurs can e-sign loan applications and get funds fast.
Hear from the bank's Director of IT Solutions Delivery about their eSignature integration and ROI.
OneSpan Sign offers Conditional Fields, giving you the power to create dynamic documents by allowing you to enforce conditional logic to your signing workflow. When creating transactions, you have the
Leverage OneSpan experts to develop, launch, and maintain an intuitive, secure mobile authenticator customized to your needs and powered by OneSpan’s award-winning Mobile Security Suite.
How OneSpan Sign for Pegasystem Works It’s easy to add e-signatures to any workflow with the Pega Designer Studio. Simply drag-and-drop the OneSpan Sign Smart Shape directly into any new or existing
Automate your digital documents and forms by adding e-signatures with OneSpan Sign for Laserfiche.
Send documents for eSignature from your on-premises instance of Guidewire PolicyCenter.
Send documents for eSignature from your on-premises instance of Guidewire ClaimCenter.
Deliver frictionless sign-up processes for your policy holders along with an easy, secure, and seamless way to manage their business applications with OneSpan Sign for Guidewire PolicyCenter™.
Digitize your claims lifecycle management process from end-to-end by erasing the manual process of signing documents with ink and paper with OneSpan Sign for Guidewire ClaimCenter™.
EagleBank cut customer onboarding from 4 days to 5 minutes with software authentication. Learn how this midsized bank modernized the authentication experience.
This guide outlines a best practices approach to protecting against account takeover fraud with proven technologies such as machine learning-based risk analytics.
App Shielding by OneSpan proactively protects against targeted attacks by blocking the foreign code from working or shutting down the application if a threat to data exists.
OneSpan modernized Raiffeisen Italy’s authentication system to comply with the revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2).
Mobile Security Suite is an all-in-one developer’s toolkit designed to improve security and user convenience across your mobile application ecosystem.
Digipass 772 with patented Cronto technology offers banks a highly secure e-signature solution while end users enjoy an exceptional user convenience.
Authentication Server Framework is an API-based authentication platform that serves as a backend for OneSpan’s strong authentication and e-signatures solutions.
OneSpan Authentication Server Appliance is a comprehensive, centralized and flexible authentication appliance designed to deliver complete authentication lifecycle management via a single, integrated
Authentication Server offers secure and seamless access to a variety of corporate resources and (banking) applications, from SSL VPNs to cloud-based apps.
This leading Saudi bank provides secure two-factor authentication (2FA) for corporate and retail clients with Digipass 260 one time passcode OTP authenticators.
P&V Insurance transformed and digitized their business with e-signatures to ensure a fully digital flow across systems, channels, and operations.
Learn how eSignatures revolutionized mobile commercial loan application for BDC without compromising security.
Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) lays the groundwork for e-signatures as a shared service.
Digipass 831 is a popular and user-friendly card reader suited for large deployments, combining smart card reader functions.
Digipass 865 is the USB connectable version of the trusted Digipass 810 The device can be used in both connected and unconnected mode.
Digipass 785 provides strong mobile security while delivering a frictionless user experience thanks to Bluetooth technology. The device offers a large color display to easily verify transaction
Digipass 310 provides banks and other organizations with a comprehensive high performance two-factor authentication solution to protect agains man-in-the-middle attacks and similar fraud schemes.
Digipass 310 provides banks and other organizations with a comprehensive high performance two-factor authentication solution to protect agains man-in-the-middle attacks and similar fraud schemes.
Digipass 300 Comfort is a large-scale security device designed those users who prefer a bigger display.
Providing an ultimate user experience, Digipass 275 is a highly efficient, cost-effective and high-volume solution for any financial organization.
Designed for mass deployments, Digipass 270 Xpress offers e-signature and one-time password (OTP) functionality.
The small and lightweight Digipass 260 offers secure remote access and authentication features. On top of that it has a streamlined design, which can be customized according to your marketing needs.
The small and lightweight Digipass 250 offers secure remote access and authentication features.
Completely digitize your workflows and cases by adding e-signatures to your documents, contracts, and more with OneSpan Sign for Pegasystems.
Secure Your Digipass® SecureClick with your Google account using this guide.
Increase security and convenience with one click secure authentication for PCs and other mobile devices supporting BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy).
Digipass SecureClick is a FIDO U2F BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) device that enables users to securely complete access to their online applications on PCs or any BLE device.
Digipass 840 Comfort Voice is a user friendly solution for people with disabilities that combines OneSpan Class 1 stand-alone smart card reader functions such as e-signature with EMV-CAP.
Front view of the DIGIPASS 920
Manual to set up DIGIPASS 920 cradle.
Digipass 920 offers high level security to banks to protect high value transactions. Its ‘What You See is What You Sign’ feature and reader signature ensures security is guaranteed at both ends of the
Please note that this driver download is for the following DP Products: Digipass 870, Digipass 920
Digipass 905 is an USB desktop smart card reader/writer. The device has a modern and ergonomic design, targeted to be used in an office or home environment.
Downloadable Zip file
Downloadable Zip file suitable for Mac OS.
Digipass 870 is a USB connectable personal card reader which can be used in both connected and unconnected mode.
DP836 - Bedienungsanleitung und Funktionsweise
DP836 A4 - Bedienungsanleitung und Funktionsweise
Digipass 830 combines all OneSpan’s Class 1 standalone smart card reader functions with EMV-CAP compliance (Europay-Mastercard-Visa Chip Authentication Program).
Digipass 810 provides a flexible, secure way to authenticate your users. Smart cards also provide an extra layer of security, because users must know a password or PIN and must have the actual card to
This document describes how you can enhance protection for online and mobile banking transactions with DIGIPASS 875.
Declaration of Conformity for DIGIPASS 875.
Bluetooth® Smart-enabled smart card reader for smartphones and tablets delivers powerful and portable mobile transaction protection
Digipass 882 is an advanced transaction signing device that combines a secure smart card reader with patented Cronto technology that leverages the latest in visual cryptogram security.
Digipass 280 is a strong authentication device that boosts security while providing unmatched user acceptance. The size of a credit card, Digipass 280 offers ultimate user convenience and can be
Digipass 281 is a strong authentication device that boosts security while providing unmatched user acceptance.
Digipass 836 reduces the level of user interaction for authentication, resulting in increased user acceptance for the use of e-signatures in high-risk internet banking transactions.
Digipass 301 Comfort Voice provides for visually impaired users unparalleled secure accessibility to telephone banking, Internet banking and e-commerce services.
The small and lightweight Digipass 270 offers the same secure remote access and authentication features of Digipass 250/260-but is extremely compact.
Digipass 760 is a patented visual transaction signing solution targeted towards online banking services. Its innovative technology is simple, user friendly and effective.
Digipass 770 with patented Cronto technology offers banks a highly secure e-signature solution allowing them to deploy or transition economically to next generation authentication methods.
Digipass GO 100 series display cards offer strong authentication that boosts security while providing unmatched user acceptance. With its credit card size form factor, Digipass GO display cards are
DEA regulations mandate the use of two-factor authentication when a prescription for a controlled substance is submitted electronically.
Digipass GO 7 is a FIPS 140-2 Level 2 Certified one-time password (OTP) hardware token – a convenient single-button authentication device that boosts security while providing unmatched user acceptance
Digipass GO 6 is a "one-button" authenticator to effectively combat internet fraud by replacing static or paper-based password systems.
Digipass GO 3 is very affordable, ultra-user friendly, and quick and efficient to rollout to users. These advantages allow you to close all security gaps in user authentication in a matter of hours.
In this video tutorial, we’ll show you how easy it is to sign a document from an email using OneSpan Sign.
SMBC improved the accessibility of its SMBC Direct online banking service with an audio one-time password (OTP) authenticator for visually impaired customers.
Acquire more customers, reduce abandonment and mitigate fraud with digital identity verification services
TUI Group needed an electronic signature provider for contract signing. Requirements included EU data hosting, legal enforceability, and Bulk Send.
Square Enix Co., Ltd. implemented OneSpan’s Digipass® GO6 for the first time in the gaming industry in Japan to prevent fraud in online games.
This white paper presents the business rationale for mobile app shielding and explains how app shielding with runtime-protection is key to developing a secure, resilient mobile banking app.
Bank of Cyprus deployed software authentication and transaction-specific one-time passcodes (OTP) for PSD2. See how the authentication flows work.
Build trust and drive growth by strengthening your mobile apps’ resistance to intrusion, tampering and reverse-engineering.
See how FIDO supports multi factor authentication by integrating face recognition, fingerprint, or other biometric authentication methods to create an exceptional customer experience for mobile and
Learn how OneSpan Sign balances ease of use with the highest levels of security.
Learn how to automate high volume customer transactions and signing workflows from start to finish with the OneSpan Sign Enterprise Plan.
The OneSpan Sign Professional Plan is packed with productivity features right out of the box, making it fast and easy to prepare and send documents for signing.
Investec uses e-signature and digital identity verification to digitize the auto finance process. Ease of use and the audit trail were must-have requirements.
These three North American banks migrated from one-time passcode (OTP) hardware authenticators to software authentication. Learn their best practices.
See how to send reminders to your signers and set an expiry date on transactions.
OneSpan Sign offers Optional Signatures to give your signers the flexibility to complete a transaction without having them sign all the signature fields in the documents.
Approximately 40% of the business is now automated and hits the books without anyone seeing or touching it.
OneSpan Mobile Authenticator is a mobile, two-factor authentication app that enables users to securely login to applications, via their mobile device, with a simple fingerprint or PIN along with a one
OneSpan Mobile Authenticator SMS offers a user-friendly and cost efficient solution for strong user authentication and e-signatures.
OneSpan Mobile Authenticator Studio balances the need for stronger application security with demands for user convenience by delivering comprehensive, built-in security for your mobile applications.
Qatargas relies on Digipass GO 6 to enable secure remote network access for employees without affecting the integrity of the computer systems and data.
Phishing and fraud are growing. To counter this, SMBC uses Digipass 275 authenticators. These 2FA devices provide user friendly, cost effective authentication.
Mizuho Corporate Bank implemented OneSpan's Digipass, a two-factor authentication (2FA) solution that complies with government guidelines.
As one of the leading banks in Azerbaijan, AGBank was looking for a security solution for its Internet and mobile banking services.
To protect their mobile banking application, they integrated the OneSpan Mobile Security Suite with all the necessary building blocks to protect an application.
Mizuho Bank secures their online banking services with OneSpan Digipass 275 authenticators. Its transaction authorization functionality helps reduce fraud.
Sony Bank uses OneSpan’s Digipass authenticators for two-factor authentication (2FA) at login, to protect against phishing attacks.
OneSpan Sign for Laserfiche allows you to prepare, manage, and send documents for e-signature directly from Laserfiche. Using OneSpan Sign for Laserfiche, you can now better collaborate with your
This 6-page white paper shares security best practices for electronic signatures. Includes a security requirements checklist.
Raiffeisen Italy modernized their authentication system to comply with the revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2). As part of that initiative, Raiffeisen Italy introduced a mobile app that
This top 20 financial institution launched a Digital Enterprise initiative in order to provide a modern customer experience. Within that initiative, the customer wanted to standardize on an e
OneSpan Sign is trusted by top banks, insurance companies and government agencies for their demanding and high volume B2C processes.
Our simple, powerful REST API and SDKs enable you to add e-signing capabilities to your website, mobile app and core systems.
For digital capabilities that impact the entire organization, like e-signature, the most competitive companies are prioritizing a shared services approach over siloed implementations.
This company compared 10 eSignature providers, made the switch, and saved 75% vs Docusign's renewal price.
OneSpan Sign is the cost-effective, enterprise-grade eSignature solution that businesses love.
Download eSignLive for Nintex SharePoint to easily obtain secure and compliant e-signatures for your contracts and documents– all while keeping your workflows fully digital. eSignLive for Nintex
Download OneSpan Sign Print Driver to easily sign documents directly in OneSpan Sign from 3rd party application.
In this video tutorial, we’ll show you how easy it is to sign transactions from the OneSpan Sign Dashboard.
In this step-by-step video tutorial, we’ll show you how to automatically extract signatures and fields using Text Tags in eSignLive.
OneSpan Sign for Finastra enables lenders to send loan origination documents to clients for e-signatures directly from LaserPro.
See how to electronically notarize documents with the eNotary feature in OneSpan Sign.
OneSpan Sign for Conga enables you to prepare, manage and send your Conga documents, contracts and more for electronic signatures directly from Salesforce.
In this on-demand webinar, you'll hear practical advice from GAINSCO Auto Insurance on e-signature adoption and how to reduce risk while streamlining key processes for maximum ROI from your e
eSignature authentication ensures trusted transactions for any process, channel, and risk level. See the top 10 methods.
Learn how to distribute documents for signature using a single URL with the Fast Track feature.
See how to control which documents your recipients can view and sign in a transaction.
Get a complimentary copy of the Celent report on Bank of Montreal's eSignature and eForms enterprise-wide deployment.
OneSpan Sign supports signing with digital certificates stored on government-issued smart cards.
In this step-by-step video tutorial, we'll show you how easy it is to create and use layouts in OneSpan Sign.
See how easy it is to delegate signing authority to others in your organization with the access delegation feature.
See how easy it is to authenticate a signer's identity to access documents and sign with OneSpan Sign.
See how easy it is to send a document to multiple recipients at once using the bulk send feature.
See how easy it is to send documents directly to OneSpan Sign from virtually any 3rd party app.
See how to use dashboards to manage eSignature transactions in OneSpan Sign.
In this step-by-step video tutorial, we'll show you how to create and use templates in OneSpan Sign.
Learn how easy it is to send a document for signature using OneSpan Sign
Learn how this P&C carrier integrated e-signatures with their agent portal and made it easier for independent agents to do business.
Credit unions using the MeridianLink LoansPQ and Xpress Accounts platform can now e-sign from within MeridianLink’s workflow.
An overview of e-signature laws, regulations, and standards for financial services.
Digital signatures and electronic signatures have become commonplace, but there is often confusion between the terms. Learn the differences and core elements of both kinds of signatures.
There is a lot at stake when creating a digital or mobile eSign experience. The workflow choices you make determine user adoption - and ultimately, project success.
Learn how NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab digitized their contract process with OneSpan Sign e-signatures. Get detailed insight into their e-signature evaluation.
Watch this feature demo video to learn how easy it is to use mobile to sign documents on the go.
OneSpan Sign for Salesforce is an out-of-the-box eSignature integration that modernizes and streamlines the document signing process directly in your favorite CRM.
Learn the top user identity verification and authentication methods for secure digital transactions
Learn how to use eSignatures to improve the CX and secure digital agreements in an increasingly remote world.
Learn how to use hard and soft ROI to support your business case.
Learn the top 4 e-signature insights for broker-dealers, as told through the story of PlanMember, a broker-dealer that automated new account enrollments using OneSpan Sign integrated with Laser App.
Find out how a top U.S. Bank integrated e-signatures for Treasury Management processes in less than a week.
The IT department of a major hospital in Belgium uses OneSpan Sign electronic signature technology to e-sign from anywhere.
How one bank integrated deposit account opening processes with OneSpan Sign in just days. Now 90 percent of their customers e-sign instead of using pen and paper.
After identifying multiple requests for e-signatures within various lines of business, the bank took an enterprise approach and standardized on a single electronic signature solution for all of its
This top 50 insurance carrier has made electronic applications and signatures available to its 2,200 field agents has resulted in an impressive 75 percent adoption.
A Top 5 US Bank deploys OneSpan e-signatures across 3,000+ branches and processes 7,000 loans per week.
This case study features a student loan authority that delivers over $1.2 billion in financial aid each year through grants, scholarships and loans. Delays caused by processing paper resulted in a
Find out what happened when the GSA mandated 19,000 vendors use OneSpan Sign for billions of dollars worth of procurement contracts - a bold move towards the agency's goal for a zero environmental
By adopting electronic signatures enterprise-wide across multiple channels and lines of business, this P&C company expects to save $2.5 - $5M annually.
This essential guide introduces important legal concepts and key considerations when creating digital business processes with eSignatures.